But does the extended brewing time of cold brew translate into a higher caffeine content compared to traditional hot coffee?
Let’s examine the factors influencing the caffeine levels in this popular beverage, Does Cold Brew Coffee Have More Caffeine?
Importance of Knowing Caffeine Content in Cold Brew Coffee
Cold brew coffee, known for its smooth and less acidic taste compared to traditional hot brewed coffee, has gained popularity both worldwide and nationally for its unique brewing method and taste profile.
Unlike regular coffee that is brewed quickly using hot water, cold brew is made by steeping coffee grounds in cold water for an extended period, usually 12-24 hours, resulting in a concentrate that is often diluted with water or milk before serving.
While cold brew coffee offers a delicious alternative to traditional coffee, understanding its caffeine content is crucial.
Unlike hot-brewed coffee, cold brew’s caffeine level isn’t immediately obvious. Factors like coffee-to-water ratio, bean type, and brewing time all significantly influence the final caffeine content.
Some people mistakenly believe that cold brew always contains an extraordinarily high amount of caffeine, while others think it has less. This can be problematic, especially for those sensitive to caffeine or with specific health conditions.
Individuals with anxiety, heart conditions, or pregnancy should be particularly aware of their cold brew intake, and seek guidance from their healthcare professionals to determine appropriate consumption levels.
Knowing how much caffeine is in your cold brew allows you to make informed choices about your beverage and avoid potential jitters, sleep disturbances, or other unwanted effects from excessive caffeine consumption.
Does Cold Brew Coffee Have More Caffeine?
Cold brew coffee generally contains more caffeine than iced coffee and espresso, but it may have slightly less caffeine than hot coffee, depending on the brand and the brewing process.
It is made by steeping coffee grounds in cold water for an extended period, which allows for a higher caffeine extraction compared to hot-brewed coffee. However, cold brew is often diluted with water or milk before serving, which can reduce its caffeine concentration.
The caffeine content in cold brew coffee is influenced by a variety of factors, each playing a significant role in the final caffeine concentration of the beverage. Here’s how each factor can affect your cold brew:
Coffee-to-Water Ratio:
The most significant impact on caffeine content comes from the coffee-to-water ratio. Cold brew coffee is often made as a concentrate, with ratios ranging widely from 1:5 to 1:18 (coffee-to-water). A higher ratio results in a stronger concentrate, which can significantly increase caffeine content.
Type of Coffee Beans:
The caffeine content also varies depending on the coffee beans used. Robusta beans, for instance, have about twice as much caffeine as Arabica beans. Therefore, the choice of bean type can significantly influence the caffeine level in your cold brew.
Brewing Time:
Cold brew coffee is steeped for an extended period, usually 12-24 hours, which can affect the caffeine extraction. A longer brewing time typically results in a higher caffeine content.
Grind Size:
The coarseness of the coffee grounds can impact the extraction process, with coarser grounds extracting less caffeine than finer grounds. This means that the grind size can indirectly influence the caffeine concentration in cold brew.
Serving Size:
The caffeine content in a serving of cold brew can vary greatly depending on the serving size, as cold brew is often consumed in larger quantities compared to hot coffee due to its smoothness and reduced bitterness.
Water Temperature:
Since cold brew uses cold water, the extraction process is slower and less efficient at extracting caffeine compared to hot water. This can result in a beverage that is perceived to have less caffeine, although this is balanced out by the longer steeping time and often higher coffee-to-water ratios used.
Dilution:
Cold brew is usually served diluted with water or milk, which can reduce the caffeine concentration per serving. However, even after dilution, the caffeine content can be quite significant, especially if the original concentrate is strong.
Understanding these factors can help you adjust the caffeine content in your cold brew to your preference. Whether you’re seeking a stronger caffeine kick or a milder beverage, manipulating variables like bean type, brewing time, and dilution can help achieve the desired outcome.
For example, a 16-ounce (473 mL) cold brew from Starbucks contains 205 mg of caffeine, while a 16-ounce (473 mL) cold brew from Dunkin’ Donuts provides 260 mg of caffeine.
In comparison, a 16-ounce (473 mL) serving of hot coffee can contain between 210-360 mg of caffeine, depending on the brand and brewing process.
Iced coffee typically contains less caffeine than hot coffee, with a 16-ounce (473 mL) serving containing around 165 mg of caffeine. A 1.5-ounce (44 mL) serving of espresso contains approximately 150 mg of caffeine.
Cold Brew Coffee Variants and their Caffeine Content

Cold brew coffee has evolved into a diverse and versatile beverage category, offering a variety of types and styles to suit different tastes and preferences.
Here are some popular types of cold brew coffee:
Instant Cold Brew Coffee:
This type involves freeze-drying or spray drying concentrated cold brew coffee, resulting in a powder that can be quickly reconstituted with cold water or milk. This method offers a convenient and fast way to enjoy cold brew without the steeping time.
Cold Brew Bags/Packs:
These are pre-filled bags with a specific amount of coarsely ground coffee, designed for steeping in cold water. They offer a convenient and mess-free way to make cold brew at home, providing an efficient steeping process and easy cleanup.
Cold Brew K-cups/Pods:
Designed for Keurig brewers, these pods contain concentrated cold brew coffee instead of regular ground coffee. They can be used to make cold brew coffee quickly by brewing with hot water and then cooling the beverage, or directly with cold water.
Cold Brew in a Box:
This is premade cold brew coffee concentrate packaged in a box, often with a built-in spigot for easy dispensing. It offers a convenient way to have cold brew on hand without needing to brew it yourself, perfect for serving multiple people or for gatherings.
Cold Brew Collagen Coffee:
This combines cold brew coffee with collagen peptides, offering the benefits of both cold brew and collagen, such as supporting skin, hair, and joint health.
Cold Brew Protein Coffee:
This type mixes cold brew coffee powder with protein powder, providing a beverage that offers both a caffeine boost and muscle-supporting benefits. It’s often consumed as a post-work workout drink or meal replacement.
Decaf Cold Brew:
Made with decaffeinated coffee beans, decaf cold brew offers the smooth taste of cold brew without the caffeine. It’s ideal for those who are sensitive to caffeine or prefer to avoid it.
Cold Brew Concentrate:
This highly concentrated cold brew is meant to be diluted with water or milk before drinking. It serves as a versatile base for creating both cold and hot coffee beverages, as well as ready-to-drink products like those pre-made bottled coffee drinks found in stores and cafes.
New Orleans Style Cold-Brew Coffee:
A unique take on cold brew that includes chicory during the steeping process, providing a distinctive flavor. It’s typically sweetened and combined with milk, resulting in a creamy and rich beverage.
Nitro Cold Brew:
This variant infuses cold brew coffee with nitrogen gas, creating a rich, creamy texture akin to that of stout beer. The nitrogen bubbles contribute to a smoother and sweeter taste, often eliminating the need for added sugar or cream. Nitro cold brew is known for its velvety mouthfeel and is typically served on tap, providing a visually appealing cascading effect as it settles in the glass.
Kyoto-Style Cold Brew:
Also known as Dutch coffee, this brewing method is characterized by its distinctive slow-dripping process, where cold water is gradually dripped over coffee grounds for several hours. Originating in Japan, Kyoto-style cold brew is known for its precision and clarity of flavor, often resulting in a more refined and aromatic cold brew coffee.
Flavored Cream Cold Brew:
Elevating the cold brew experience, this type involves serving cold brew coffee with a variety of flavored creams, such as chocolate, salted caramel, vanilla, or seasonal flavors like pumpkin cream. These flavored creams add a rich, indulgent layer to the cold brew, offering a delightful contrast to the coffee’s inherent bitterness.
Homemade Cold Brew:
Many coffee enthusiasts prefer to make cold brew coffee at home using DIY methods and home brewing kits. Homemade cold brew allows for full control over the brewing process and ingredients, resulting in a personalized and satisfying cup of coffee.
List of Ingredients in Cold Brew Coffee
The ingredients used to make cold brew coffee are quite simple and typically include:
- Coffee Beans: Many cold brew enthusiasts prefer using medium to dark roast coffee beans for a richer and more robust flavor.
- Water: Coffee grinds are steeped in cold water to make cold brew coffee. To guarantee the finest flavor and quality of the finished brew, it’s critical to use clean, filtered water.
- Sweeteners: Some people prefer to add sweeteners like sugar, honey, or syrups to their cold brew coffee to enhance sweetness.
- Cream or Milk: Adding cream or milk to cold brew coffee can help mellow out the flavor and add a creamy texture. Using any other milk substitute—coconut, almond, or dairy—depends on personal dietary preferences.
- Flavorings: Flavorings such as vanilla extract, cinnamon, or flavored syrups can be added to cold brew coffee to create unique flavor combinations. Experimenting with different flavorings allows for customization according to personal preferences.
- Ice: Ice cubes can be added directly to the cold brew or used to chill the serving glass before pouring.
Cold Brew Coffee Nutritional Information
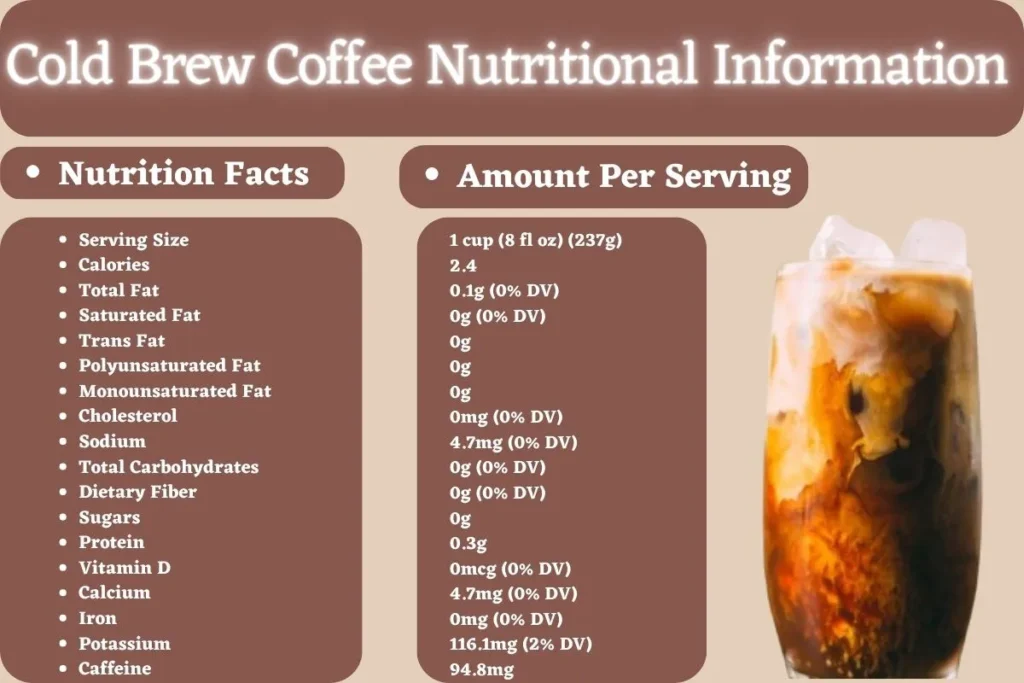
Cold brew coffee is a naturally low-calorie and low-fat beverage. A typical one cup (8 fl oz) serving contains about 2.4 calories and a negligible amount of fat. It also offers no cholesterol, sodium, carbohydrates, dietary fiber, or sugars. Cold brew does provide a small amount of protein (0.3g per serving) and trace amounts of calcium and iron. However, its primary nutritional highlight is a moderate caffeine content, providing around 94.8mg per cup.
| Nutrition Facts | Amount Per Serving |
| Serving Size | 1 cup (8 fl oz) (237g) |
| Calories | 2.4 |
| Total Fat | 0.1g (0% DV) |
| Saturated Fat | 0g (0% DV) |
| Trans Fat | 0g |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 0g |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 0g |
| Cholesterol | 0mg (0% DV) |
| Sodium | 4.7mg (0% DV) |
| Total Carbohydrates | 0g (0% DV) |
| Dietary Fiber | 0g (0% DV) |
| Sugars | 0g |
| Protein | 0.3g |
| Vitamin D | 0mcg (0% DV) |
| Calcium | 4.7mg (0% DV) |
| Iron | 0mg (0% DV) |
| Potassium | 116.1mg (2% DV) |
| Caffeine | 94.8mg |
👉Does Coffee Liqueur Have Caffeine
Alternatives to Cold Brew Coffee and their Caffeine Content
Exploring alternatives to cold brew coffee opens up a world of flavorful and varied beverage options, each with its unique caffeine content to suit different preferences and health considerations. Here’s a diverse list of alternatives along with their caffeine content:
Iced Coffee:
Iced coffee is made by brewing hot coffee and pouring it over ice. The brewing process is different from cold brew, but the flavor profile can be similar. It has about the same caffeine content as a similar volume of drip coffee. A standard 8 oz cup of iced coffee contains around 80-100 mg of caffeine.
Japanese Cold Brew:
Japanese cold brew, also known as Kyoto-style or slow-drip cold brew, is made by dripping cold water over medium/coarse ground coffee over 15-20 hours. This method highlights acidic flavor notes, providing a bright and refreshing taste. It has a caffeine content similar to cold brew, around 150-200 mg per 16 oz.
New Orleans Iced Coffee / Cold Brew:
This unique cold brew variation includes chicory, a root vegetable with a cocoa-like flavor. It’s typically served with simple syrup and cream, creating a rich and indulgent coffee experience. The caffeine content is similar to cold brew, around 150-200 mg per 16 oz.
Nitro Cold Brew:
Nitro cold brew is made by infusing cold brew coffee with nitrogen gas, creating a smooth and silky texture. The nitrogen infusion also gives the coffee a creamy head, similar to a stout beer. Nitro cold brew has 2.5 to 3 times more caffeine than a regular cup of coffee, around 200-300 mg per 16 oz.
Decaf Cold Brew:
Decaf cold brew is made by steeping decaf coffee beans in cold water for 12-24 hours. This method retains the smooth and mellow flavor profile of cold brew while significantly reducing caffeine content. A 16 oz serving of decaf cold brew typically contains 5-10 mg of caffeine.
Shaken Espresso:
Shaken espresso is a cold brew alternative that involves shaking espresso shots with ice and various flavors, such as vanilla or caramel syrup, and milk options like oat or almond milk. Shaken espresso can be made with decaf espresso for a lower caffeine option. A 16 oz serving of shaken espresso with decaf espresso contains around 10-20 mg of caffeine.
Herbal Coffee:
Herbal coffee substitutes like roasted carob, chicory, and dandelion root offer a coffee-like flavor without caffeine. These alternatives are made by roasting and grinding the roots or seeds, then brewing them like traditional coffee. A 16 oz serving of herbal coffee contains around 5-10 mg of caffeine.
Matcha Latte:
Matcha latte is a creamy and sweet alternative to cold brew. Matcha is a stone-milled green tea powder that is blended with adaptogens and probiotics for added health benefits. A 16 oz serving of matcha latte contains around 70-80 mg of caffeine.
Super Cocoa Coffee Alternative:
Super cocoa coffee alternatives combine cocoa with coffee flavors, offering a rich and flavorful option. These alternatives are made from cocoa beans and coffee beans and can be brewed like traditional coffee. A 16 oz serving of super cocoa coffee alternative contains around 5-10 mg of caffeine.
Mushroom Coffee Alternative:
Mushroom-infused coffee alternatives provide a unique flavor profile and can be a low-caffeine substitute for cold brew. These alternatives combine coffee with various mushrooms, such as chaga, lion’s mane, or reishi, for added health benefits. A 16 oz serving of mushroom coffee alternative contains around 50-60 mg of caffeine.
| Alternative to Cold Brew Coffee | Caffeine Content (per 16 oz) |
| Iced Coffee | 80-100 mg |
| Japanese Cold Brew | 150-200 mg |
| New Orleans Iced Coffee / Cold Brew | 150-200 mg |
| Nitro Cold Brew | 200-300 mg |
| Decaf Cold Brew | 5-10 mg |
| Shaken Espresso (with decaf espresso) | 10-20 mg |
| Herbal Coffee | 5-10 mg |
| Matcha Latte | 70-80 mg |
| Super Cocoa Coffee Alternative | 5-10 mg |
| Mushroom Coffee Alternative | 50-60 mg |
Recommended Daily Intake of Cold Brew Coffee
Does Cold Brew Coffee Have More Caffeine? A typical cup (8 fl oz) of cold brew coffee contains around 94.8mg of caffeine, representing about 23.7% of the recommended daily intake (RDI) of 400mg for healthy adults. This means that cold brew offers a moderate dose of caffeine compared to the RDI.
While enjoying a single cup isn’t likely to put you over your daily limit, it’s important to remember that caffeine content in cold brew can vary greatly. Different brewing methods, coffee bean strengths, and ratios can result in significantly higher caffeine levels.
Additionally, even moderately caffeinated drinks can affect caffeine-sensitive individuals. Always consider these factors and your tolerance when enjoying cold brew coffee.
Conclusion
Cold brew coffee offers a delicious and distinctive way to enjoy your daily caffeine. Its unique flavor profile and potential for a high caffeine concentration make it an appealing choice. However, it’s essential to be aware that caffeine affects everyone differently. Even with its smooth taste, cold brew can still deliver a significant jolt.
It’s best to be mindful of your overall caffeine consumption throughout the day and adjust your cold brew intake accordingly. Pay attention to how your body responds, and consider smaller serving sizes or diluting your cold brew if you find yourself overly stimulated.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is special about cold brew coffee?
Cold brew coffee has a uniquely smooth, less acidic flavor compared to traditional hot-brewed coffee. Because it’s brewed with cold or room temperature water over a long period, certain bitter compounds found in coffee beans aren’t extracted as readily. This results in a mellower, often sweeter-tasting coffee.
2. Is cold brew stronger than coffee?
Cold brew frequently has a higher caffeine concentration than regular coffee due to the higher coffee-to-water ratio used. However, the perceived strength can vary depending on how the cold brew concentrate is diluted before drinking.
3. How is cold brew different from cold coffee?
Cold brew coffee is brewed with cold or room temperature water, while iced coffee is traditional hot-brewed coffee that has been chilled. This brewing method is the key factor that gives cold brew its distinctive smoothness and lower acidity.
4. How is cold brew coffee made?
Cold brew coffee is made by steeping coarsely ground coffee beans in cold or room temperature water for 12-24 hours. After steeping, the mixture is strained to remove the grounds, leaving a concentrated cold brew coffee that can be diluted with water or milk.
5. Is cold brew coffee healthy?
Cold brew coffee shares many of the same potential health benefits as regular coffee, like improved alertness and potential protection against certain diseases. It also offers lower acidity, making it a good option for those who find traditional coffee too harsh on their stomachs. However, it’s important to be mindful of added sugars and creamers, as these can significantly change the health profile of your cold brew drink.
Know More:
👉Does Latte Have Caffeine?
👉Does Starry Have Caffeine?
👉Does Fresca Have Caffeine?
👉Does Moringa Have Caffeine?

Rossi Glover, the passionate Owner of Grand Lake Coffee, infuses every cup with her love for coffee and dedication to quality. With an extensive background in the art and science of coffee, Rossi is not just a connoisseur but a storyteller, sharing the intricate tales behind each brew.

